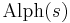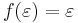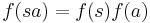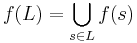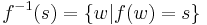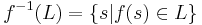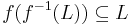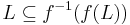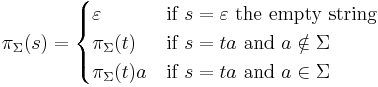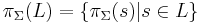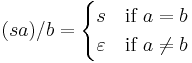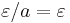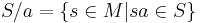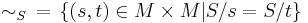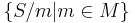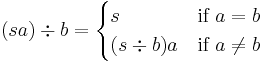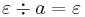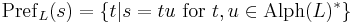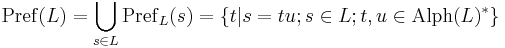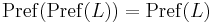String operations
In computer science, in the area of formal language theory, frequent use is made of a variety of string functions; however, the notation used is different from that used on computer programming, and some commonly used functions in the theoretical realm are rarely used when programming. This article defines some of these basic terms.
Contents |
Alphabet of a string
The alphabet of a string is a list of all of the letters that occur in a particular string. If s is a string, its alphabet is denoted by
String substitution
Let L be a language, and let 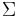 be its alphabet. A string substitution or simply a substitution is a mapping f that maps letters in
be its alphabet. A string substitution or simply a substitution is a mapping f that maps letters in 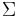 to languages (possibly in a different alphabet). Thus, for example, given a letter
to languages (possibly in a different alphabet). Thus, for example, given a letter 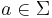 , one has
, one has 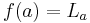 where
where 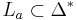 is some language whose alphabet is
is some language whose alphabet is  . This mapping may be extended to strings as
. This mapping may be extended to strings as
for the empty string 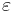 , and
, and
for string 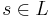 . String substitution may be extended to the entire language as
. String substitution may be extended to the entire language as
An example of string substitution occurs in regular languages, which are closed under string substitution. That is, if the letters of a regular language are substituted by other regular languages, the result is still a regular language.
Another example is the conversion of an EBCDIC-encoded string to ASCII.
String homomorphism
A string homomorphism (often referred to simply as a homomorphism in formal language theory) is a string substitution such that each letter is replaced by a single string. That is, 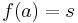 , where s is a string, for each letter a. String homomorphisms are homomorphisms, preserving the binary operation of string concatenation. Given a language L, the set
, where s is a string, for each letter a. String homomorphisms are homomorphisms, preserving the binary operation of string concatenation. Given a language L, the set 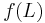 is called the homomorphic image of L. The inverse homomorphic image of a string s is defined as
is called the homomorphic image of L. The inverse homomorphic image of a string s is defined as
while the inverse homomorphic image of a language L is defined as
Note that, in general, 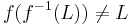 , while one does have
, while one does have
and
for any language L.
A string homomorphism is said to be 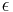 -free (or e-free) if
-free (or e-free) if 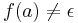 for all
for all 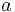 in
in 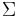 . Simple single-letter substitution ciphers are examples of (
. Simple single-letter substitution ciphers are examples of (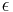 -free) string homomorphisms.
-free) string homomorphisms.
String projection
If s is a string, and 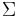 is an alphabet, the string projection of s is the string that results by removing all letters which are not in
is an alphabet, the string projection of s is the string that results by removing all letters which are not in 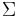 . It is written as
. It is written as 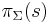 . It is formally defined by removal of letters from the right hand side:
. It is formally defined by removal of letters from the right hand side:
Here 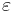 denotes the empty string. The projection of a string is essentially the same as a projection in relational algebra.
denotes the empty string. The projection of a string is essentially the same as a projection in relational algebra.
String projection may be promoted to the projection of a language. Given a formal language L, its projection is given by
Right quotient
The right quotient of a letter a from a string s is the truncation of the letter a in the string s, from the right hand side. It is denoted as 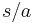 . If the string does not have a on the right hand side, the result is the empty string. Thus:
. If the string does not have a on the right hand side, the result is the empty string. Thus:
The quotient of the empty string may be taken:
Similarly, given a subset 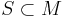 of a monoid
of a monoid  , one may define the quotient subset as
, one may define the quotient subset as
Left quotients may be defined similarly, with operations taking place on the left of a string.
Syntactic relation
The right quotient of a subset 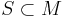 of a monoid
of a monoid  defines an equivalence relation, called the right syntactic relation of S. It is given by
defines an equivalence relation, called the right syntactic relation of S. It is given by
The relation is clearly of finite index (has a finite number of equivalence classes) if and only if the family right quotients is finite; that is, if
is finite. In this case, S is a recognizable language, that is, a language that can be recognized by a finite state automaton. This is discussed in greater detail in the article on syntactic monoids.
Right cancellation
The right cancellation of a letter a from a string s is the removal of the first occurrence of the letter a in the string s, starting from the right hand side. It is denoted as 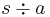 and is recursively defined as
and is recursively defined as
The empty string is always cancellable:
Clearly, right cancellation and projection commute:
Prefixes
The prefixes of a string is the set of all prefixes to a string, with respect to a given language:
here 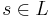 .
.
The prefix closure of a language is
Example:
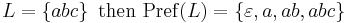
A language is called prefix closed if 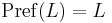 .
.
The prefix closure operator is idempotent:
The prefix relation is a binary relation 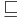 such that
such that 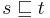 if and only if
if and only if 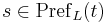 .
.
See also
References
- John E. Hopcroft and Jeffrey D. Ullman, Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages and Computation, Addison-Wesley Publishing, Reading Massachusetts, 1979. ISBN 0-201-02988-X. (See chapter 3.)